February Focus: RSD’s Heart & Thorax Phantom
Evaluate detectability, extent, and severity of myocardial infarcts in patients
RSD’s Heart & Thorax Phantom is designed to provide different reconstruction strategies, imaging protocol for patients, and testing and validation of image registration techniques. It also delivers a valid assessment of mammoscintigraphy techniques.
Myocardial perfusion SPECT is a widely used, non-invasive method for the diagnosis and management of patients with coronary disease. However, non-uniform photon attenuation, Compton scatter, limited and depth-dependent spatial resolution, as well as image noise, limit the ability of SPECT to obtain images that reliably represent the true tracer distribution. The non-uniform attenuation of the thorax is the most significant factor limiting the diagnostic efficacy of myocardial SPECT.
The currently used attenuation, scatter, and resolution correction methods are suboptimal since they do not provide improvement in the 25% false-negative findings in a group of about 100 patients with luminal diameter stenoses of at least 50%. Furthermore, the ability to detect multivessel disease was 70% without and 47% with corrections. This finding implies that myocardial SPECT can seriously underestimate the extent of disease in high-risk patients. On the other hand, the false positive findings in the group with a low probability of coronary disease were reduced from 14% without corrections to 3% with corrections.
Further improvements in both hardware and software for myocardial SPECT are necessary before this important diagnostic technique can realize its full potential. These improvements must be carefully evaluated on realistic, anthropomorphic phantoms to improve results in clinical practice.
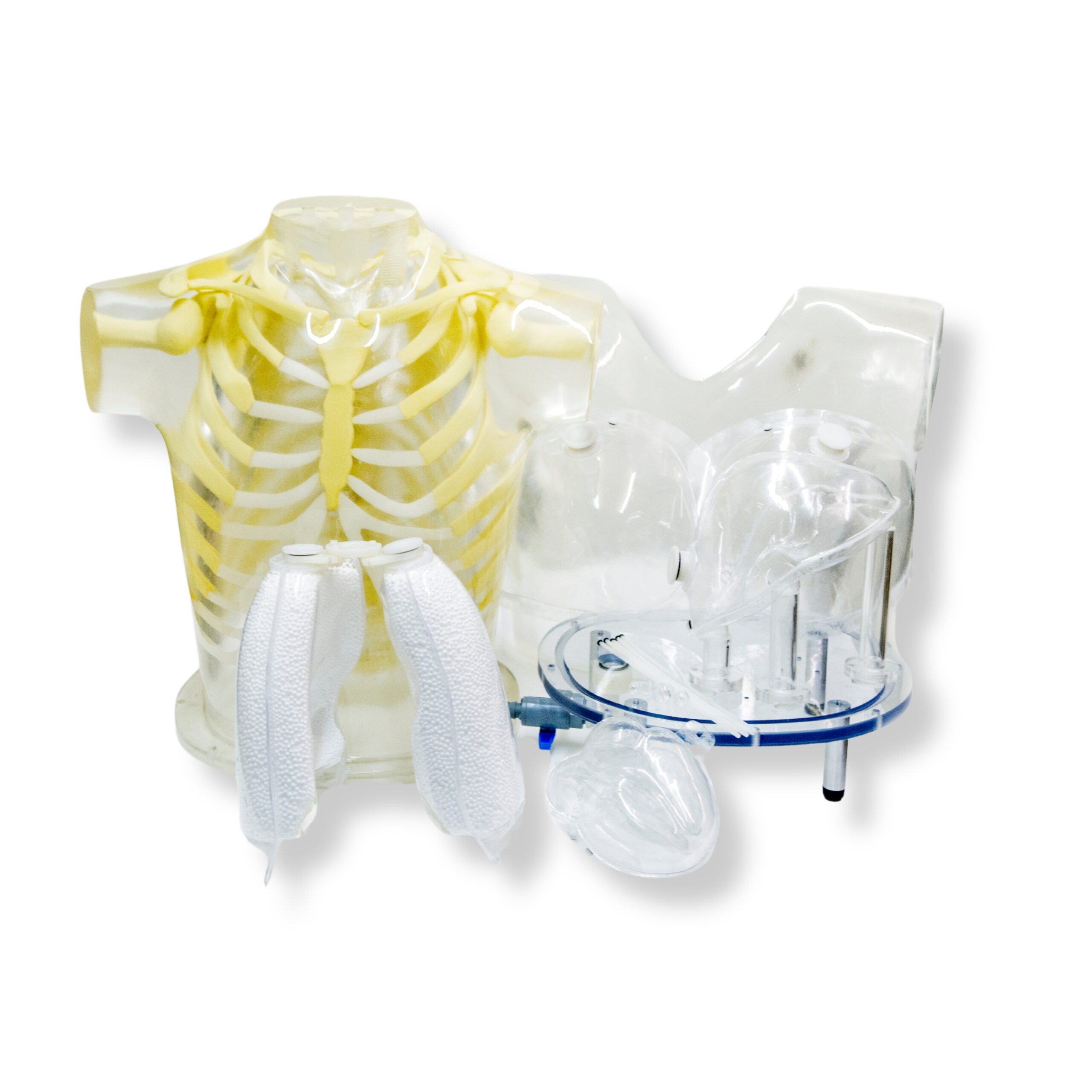
Heart Model
An accurately anatomic heart model is based on vacuum-formed shells. It was designed using high resolution, contrast-enhanced, ultrafast CT data from a normal patient, slightly modified to facilitate its use.
The left and right chambers are connected at the atrium region to make a single compartment that can be filled and flushed independently using two ports labeled HC (heart chambers). The right ventricle is slightly modified to allow air to escape during filling. The myocardial wall (MW) has two ports, flushing and independent filling. The volume of the heart chambers is 284 ml, while the volume of the myocardial wall is 238 ml, without inserted defects.
The standard model includes three defects with volumes of 8.9, 13.5, and 41.7 ml, respectively. Each of the defects can be filled separately.
Defects of different dimensions can be ordered at no added cost. A disassembled heart is sent on request so that dimensions of a special set can be established. Note that different defects cannot be retrofitted in the assembled heart.
LEARN MORERSD Is Taking New Orders!
From new product development, enhancements, or custom-built solutions, RSD is your trusted partner for product design, engineering, and manufacturing for all imaging modalities. Click below to get started!